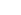
A liquid nitrogen container is a specialized container used to store and transport liquid nitrogen. Liquid nitrogen is an extremely cold substance (-196°C/-321°F), and it can cause severe damage to living tissues and materials that are not designed to withstand extreme cold.
Liquid nitrogen containers are designed to be well-insulated, typically with a vacuum layer between the inner and outer walls of the container, to minimize the loss of the extremely cold temperature of the liquid nitrogen. They are also usually made of materials that are able to withstand the low temperatures and prevent the container from cracking or becoming brittle, such as stainless steel or aluminum.
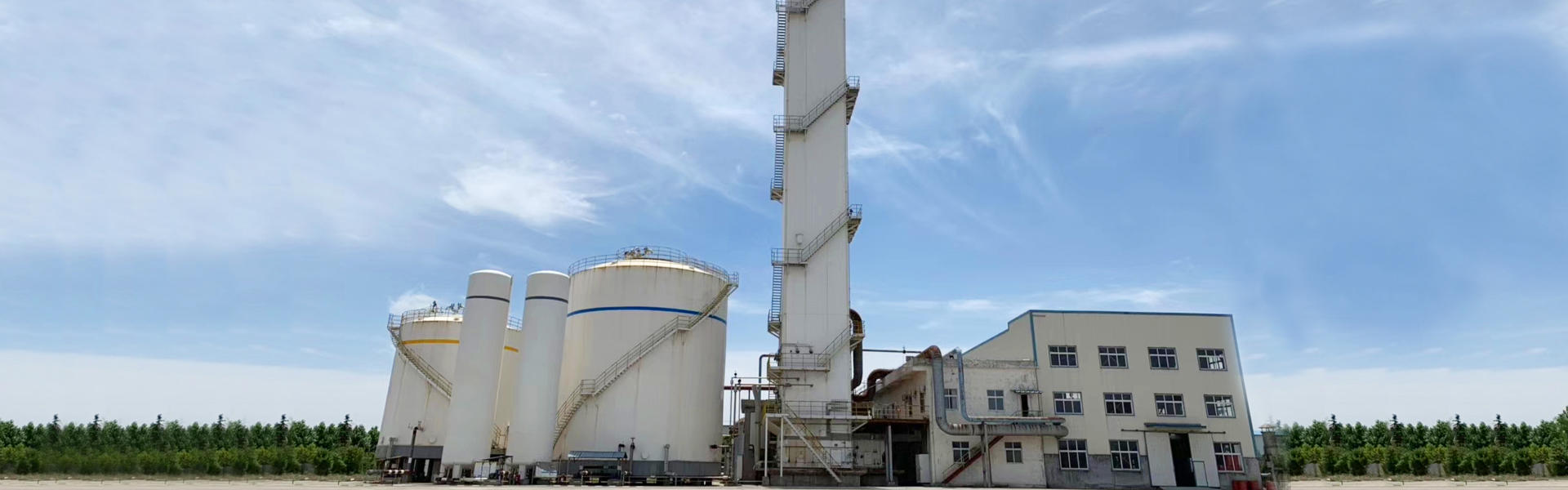
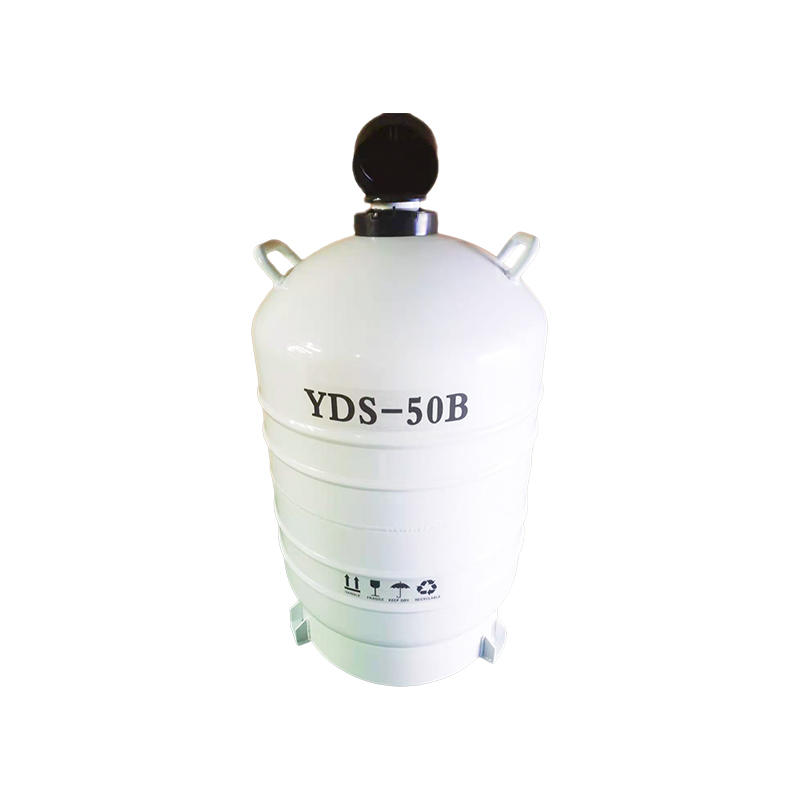
There are different types of liquid nitrogen containers, including dewars and cryogenic tanks. Dewars are smaller, portable containers that are commonly used for laboratory and medical applications, while cryogenic tanks are larger, stationary containers that are used in industrial settings.
When handling liquid nitrogen, it is important to take appropriate safety precautions, including wearing protective clothing and eyewear, working in well-ventilated areas, and ensuring that the container is properly labeled and stored.
Liquid nitrogen is a cryogenic liquid that is commonly used in laboratories, medical facilities, and other settings to store and transport biological samples, cells, tissues, and other materials at very low temperatures. To use a liquid nitrogen container safely, follow these steps:
Safety precautions: Make sure to wear appropriate protective gear, including cryogenic gloves and eye protection, when handling liquid nitrogen. Also, ensure that the area around the container is well-ventilated and free of any flammable materials.
Filling the container: To fill the container, slowly pour the liquid nitrogen into the container until it reaches the desired level. Be careful not to overfill the container, as this can cause the liquid nitrogen to spill out and potentially cause injury.
Storing the samples: Once the container is filled, carefully place the samples in the liquid nitrogen, making sure they are fully submerged. Avoid dropping the samples into the liquid nitrogen, as this can cause splashing and potentially cause injury.
Closing the container: Make sure the container lid is securely fastened, and use the locking mechanism if provided. This will prevent the liquid nitrogen from evaporating too quickly and help maintain the low temperature inside the container.
Labeling the container: It is important to label the container with the type of samples stored, the date of storage, and any other relevant information. This will help you keep track of the samples and ensure that they are properly maintained.
Monitoring the container: Check the container regularly to ensure that the liquid nitrogen level is maintained and that there are no signs of leakage or other issues. If you notice any problems, stop using the container immediately and seek professional help to resolve the issue.
Remember that liquid nitrogen is extremely cold and can cause serious injury or even death if mishandled. Always use caution when handling and storing liquid nitrogen, and seek professional advice if you are unsure about any aspect of the process.