Industry knowledge
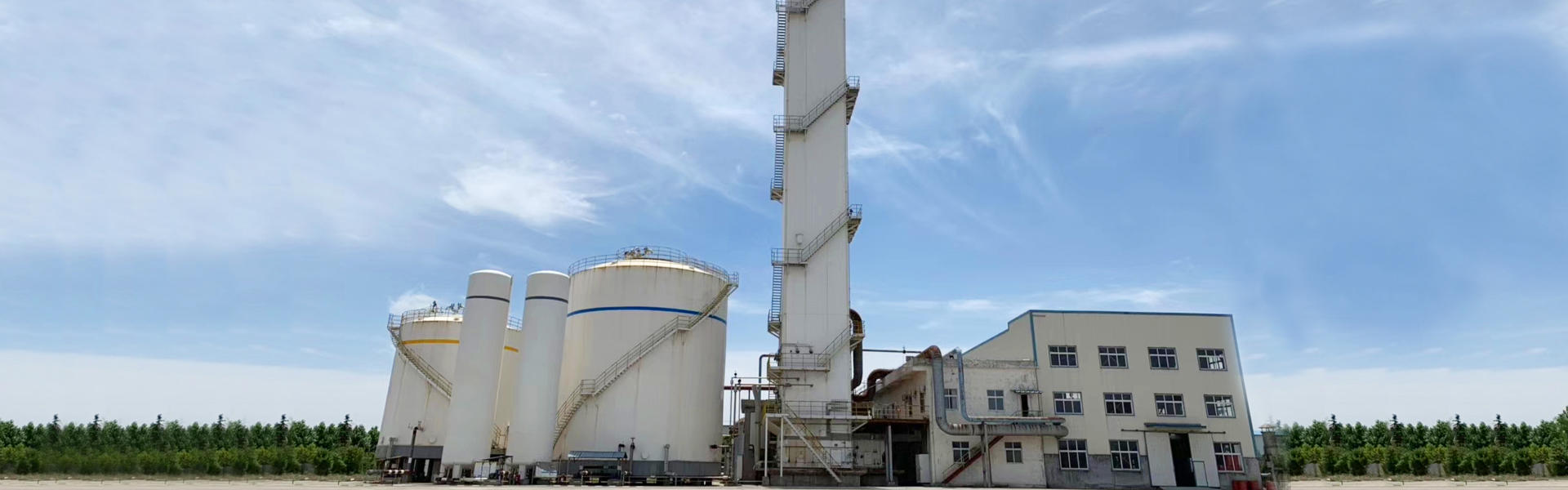
An ambient air vaporizer is a device that is used to vaporize liquid gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide. It operates on the principle of heat exchange, where the ambient air is used as the source of heat to vaporize the liquid gas.
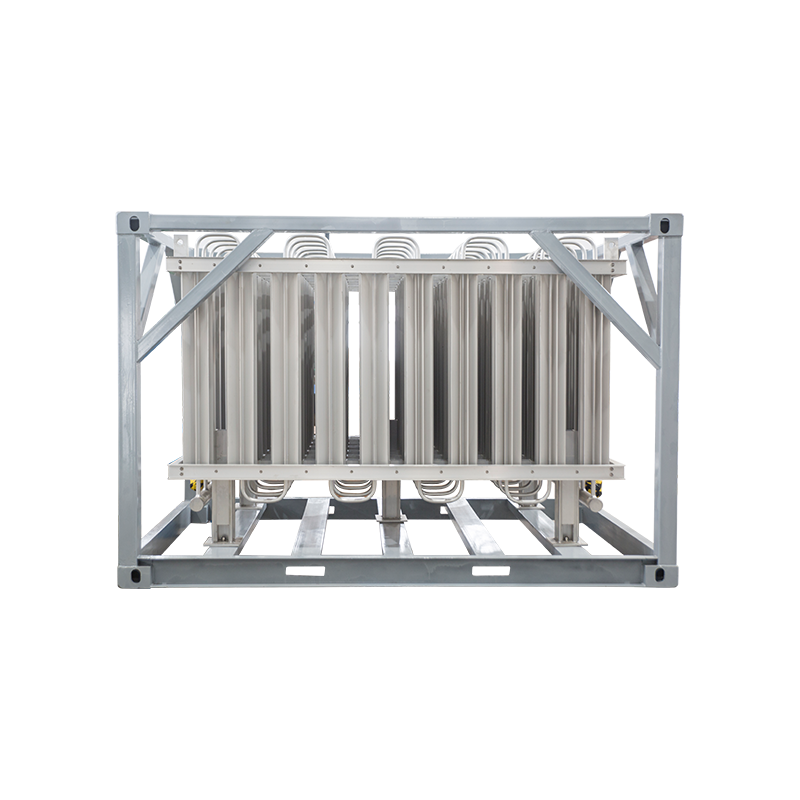
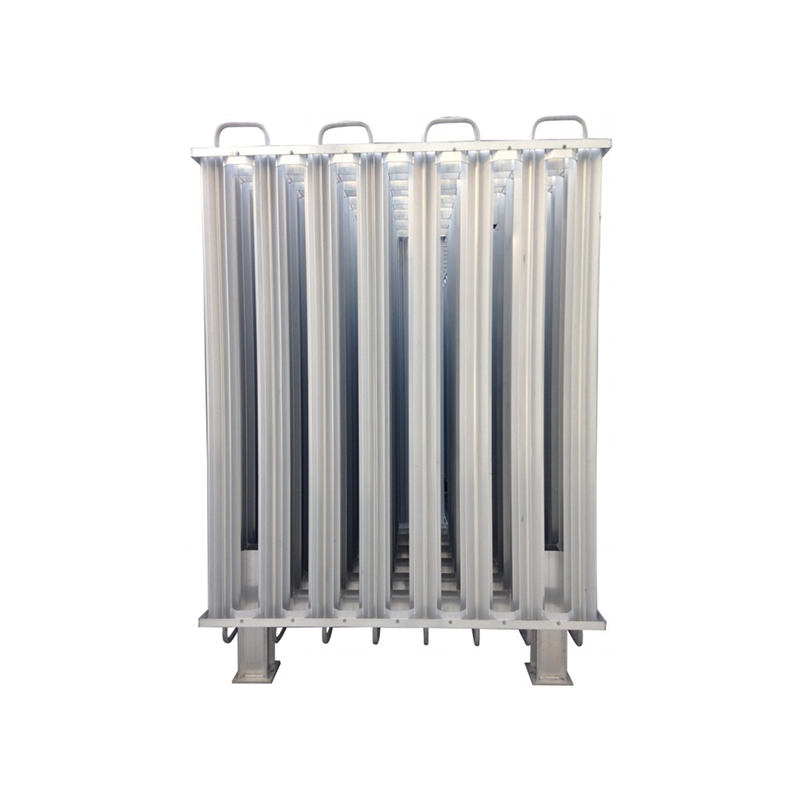
The device consists of a heat exchanger that is designed to transfer heat from the ambient air to the liquid gas, causing it to vaporize. The heat exchanger typically comprises a series of finned tubes that allow for efficient heat transfer. The liquid gas is circulated through the tubes while the ambient air is blown over the fins to transfer heat to the tubes.
Ambient air vaporizers are commonly used in industrial applications such as gas storage and distribution, as well as in cryogenic applications such as the cooling of superconducting magnets. They are preferred over other types of vaporizers such as electric or steam vaporizers because they do not require an external source of power or steam.
However, one limitation of ambient air vaporizers is that they are less efficient than other types of vaporizers, and may not be suitable for applications that require high flow rates or high vaporization rates. Additionally, they may be affected by changes in ambient temperature and humidity, which can impact their performance.
An ambient air vaporizer is a device used to vaporize cryogenic liquids, such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), by using ambient air to transfer heat to the cryogenic liquid. The following steps will guide you on how to use an ambient air vaporizer:
Connect the vaporizer to the cryogenic liquid storage tank using suitable connectors and hoses.
Ensure that the ambient air inlet and outlet openings of the vaporizer are clear and unobstructed.
Open the cryogenic liquid valve to allow the liquid to flow into the vaporizer.
Check the pressure and temperature of the liquid inside the vaporizer.
Turn on the fan or blower to draw in ambient air into the vaporizer. The air will pass over the heat exchange tubes and transfer heat to the cryogenic liquid, causing it to vaporize.
Monitor the temperature and pressure of the vaporized gas leaving the vaporizer. The temperature and pressure should be within the desired range for the application.
Adjust the fan or blower speed to maintain the desired temperature and pressure of the vaporized gas.
When the cryogenic liquid is fully vaporized, close the liquid valve and turn off the fan or blower.
Disconnect the vaporizer from the cryogenic liquid storage tank and store it properly.
It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and safety guidelines when using an ambient air vaporizer to ensure safe and efficient operation.